Are you looking to learn what scientists have discovered about how people learn, and how to apply this information to your work in a school or classroom?
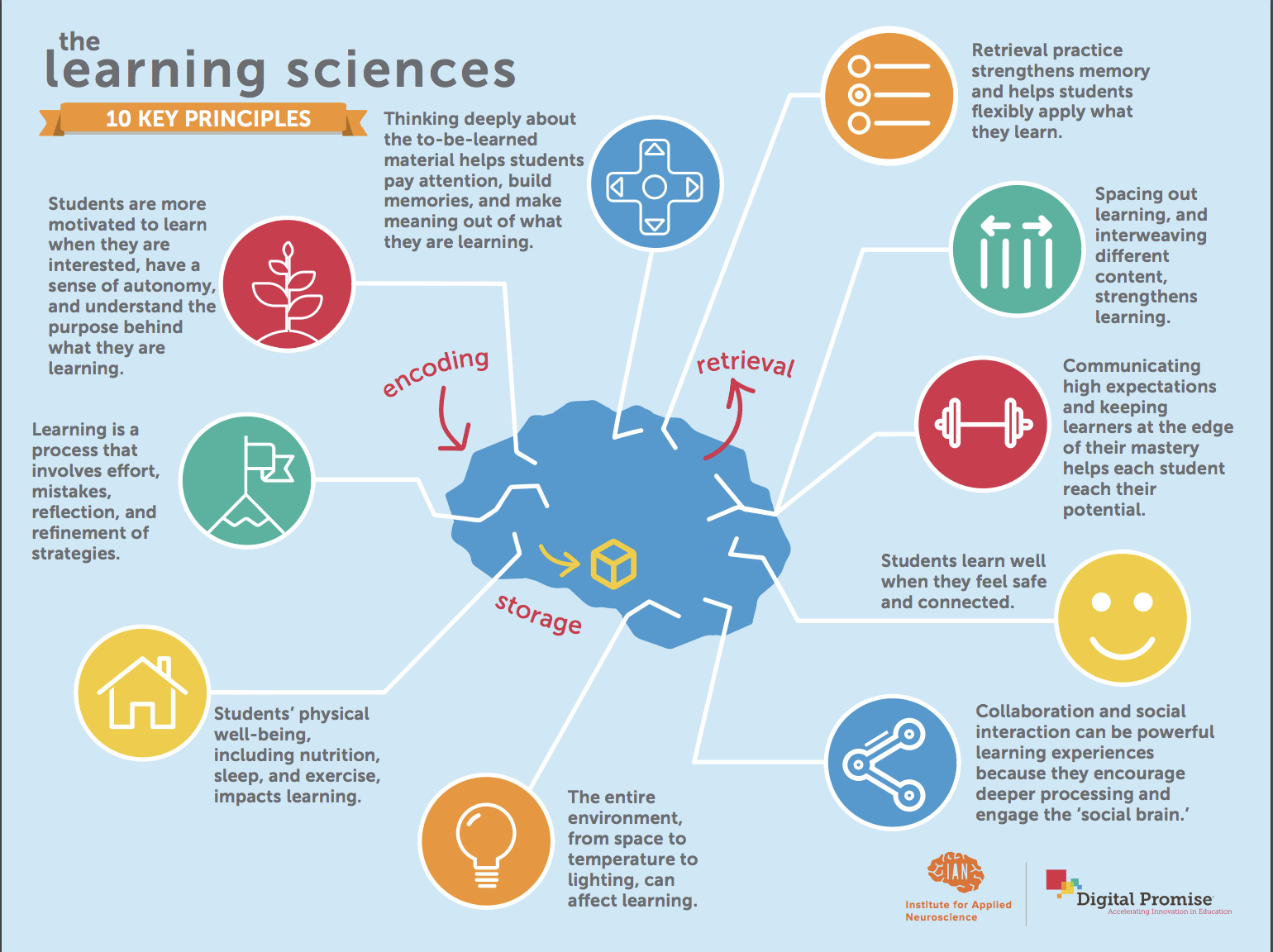
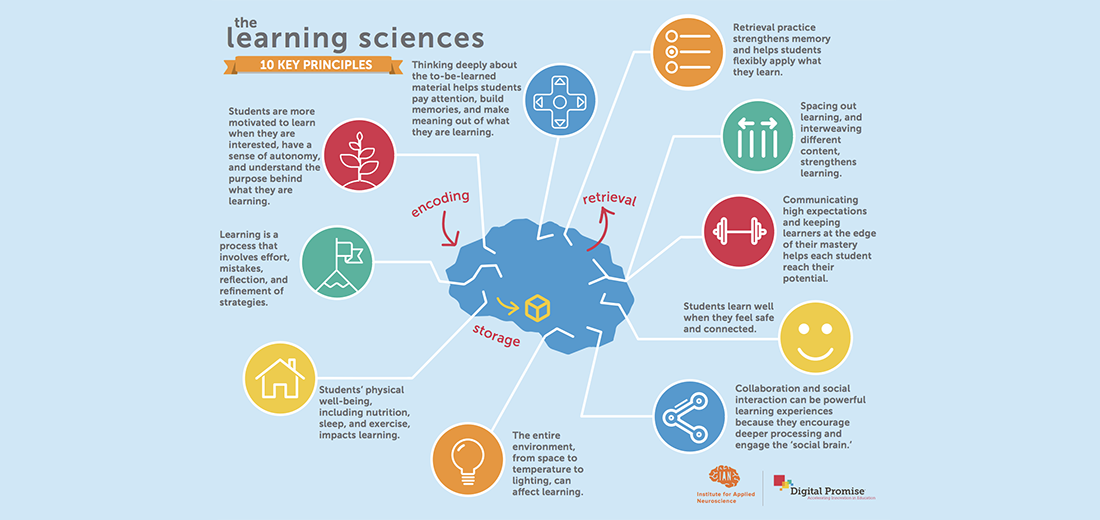
Neuroscience research has shown that learning in the brain happens in three phases: encoding (transforming experience into long-term memory), consolidation (storing and maintaining information over time) and retrieval (accessing information when needed). Additionally, researchers have discovered that the environment in which students learn, including the physical space as well as social and emotional factors, can impact learning.
Digital Promise and the Institute for Applied Neuroscience have teamed up to synthesize findings from the growing field of learning sciences research into 10 key insights about how people learn, along with suggestions for how to apply this information to classroom practice. Download these resources in the form of a poster to hang on your classroom wall, or a set of cards to take on-the-go. Below, click to expand each learning sciences insight to access more detail on the research and tips to apply it in practice.
Click each insight for more information about what the research shows and for tips on how to apply the insight in practice.
Insight:
Learning is a continual process that leads to the development of new knowledge as well as changes in existing knowledge. Helping students understand that many aspects of learning, including strategy and effort, are under their control fosters students’ beliefs in their own agency to learn. When students see failure as an opportunity to find out what they do not know (and adjust their learning strategies accordingly), rather than as an indication of self-worth, they are more likely to persevere. Students may also appreciate learning more about the processes that other insights in this series explain.
In Practice:
Insight:
When students are invited to think deeply about subject matter, they can better build strong memories. Deep thinking and a focus on making connections also allow students the time to make meaningful connections between the material, their own lives, and the world around them. When students see how material relates to their lives and interests as well as other concepts they already know, they have frameworks for understanding the material more easily and can learn it more deeply.
In Practice:
Insight:
To foster deeper learning, the learning process needs to be productively difficult. Learning is like sports: while practice is not always fun and drills can be difficult, a deliberate training process leads to improvement. Having students work at the edge of their mastery while maintaining high expectations pushes them past their current abilities, engages the brain deeply, and lays the foundation for strong learning.
In Practice:
Insight:
Retrieval activities, like self-testing and low-stakes quizzing, that ask students to practice remembering the information they’ve been taught by retrieving it from their long-term memory actually change the nature of memory by strengthening the path to memory and enriching the memory itself. In this way, retrieval practice leads to stronger and more enduring learning.
In Practice:
In Practice:
Insight:
The level of a student’s interest has been shown to be a powerful influence on learning. Additionally, when students have a sense of control over their own learning, and the opportunity to set goals that are not only personally meaningful but also have the potential to benefit the world, their intrinsic motivation improves. As a result, they are more likely to persist longer at academic tasks and to process information more deeply. Motivation does not replace the important foundational importance of helping a learner engage in behaviors that help them encode, consolidate, and retrieve memories. Likewise, engagement should be directed toward the actual material to be learned.
In Practice:
Insight:
When students feel that they are part of a positive, supportive learning community, this can reduce anxiety, allowing them to focus on learning. Building stable, trusting relationships with students supports their self-worth and promotes their sense of belonging.
In Practice:
Insight:
Students are highly tuned to social dynamics and research shows that certain collaborative and relational interactions can drive learning. Harnessing this social drive in the classroom can take students further than they can go alone. Working collaboratively towards a common goal, rather than dividing a project into parts that can be done individually, encourages students to discuss, think about ideas they might not have considered, and learn more than they would if working individually.
In Practice:
Insight:
Learning will be impaired if students’ basic physiological needs are not met. Students with good overall physical well-being have better cognitive skills than when they are in poor condition. Aerobic exercise can transiently improve the brain’s plasticity and can increase hippocampal volume (a key part of the brain involved in learning new information). Sleep is critical for solidifying learning from the day, and is one of the most important (and easiest) ways to strengthen learning. Basic nutrition is also important for brain health.
In Practice:
Insight:
Elements of the physical environment can play a role in determining whether the classroom will be conducive for focus and learning. Exposure to sunlight, as well as views of nature from the classroom, has been shown to boost student achievement, well-being, and behavior.
In Practice:

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.